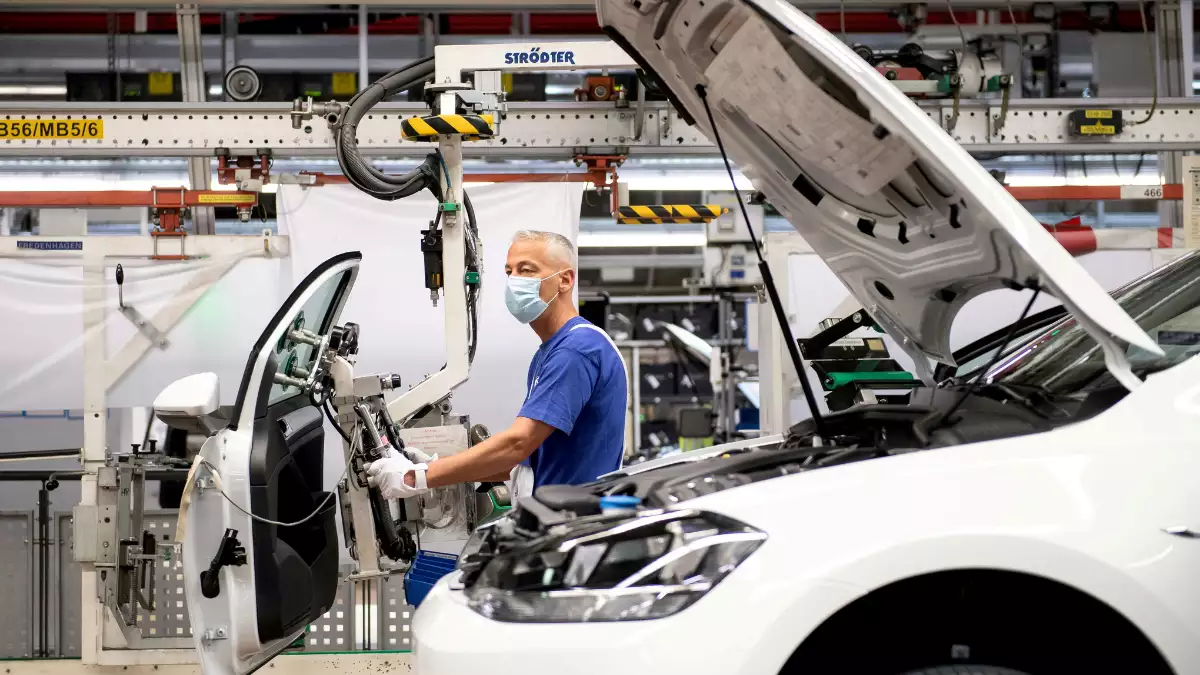
Automobile engineering, also known as automotive engineering, is a multidisciplinary field that encompasses the design, development, manufacturing, and maintenance of automobiles. It plays a pivotal role in the transportation industry, constantly striving to enhance vehicle performance, safety, and sustainability. This article delves into the fascinating world of automobile engineering, exploring its historical origins, core principles, technological advancements, and future prospects.
I. Historical Origins:
The roots of automobile engineering can be traced back to the late 19th century when the first self-propelled vehicles were introduced. Innovators like Karl Benz and Henry Ford pioneered the mass production of automobiles, revolutionizing transportation forever. Since then, the industry has undergone significant transformations, driven by advancements in materials, propulsion systems, electronics, and automation.
II. Core Principles:
Vehicle Design: Automobile engineers focus on designing vehicles that balance aesthetics, functionality, and aerodynamics. They employ computer-aided design (CAD) software to develop 3D models, optimizing vehicle performance, occupant safety, and fuel efficiency.
Powertrain Systems: Powertrain refers to the mechanism that converts the engine’s power into motion. It includes the engine, transmission, driveshaft, differential, and axles. Automobile engineers strive to improve powertrain efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance performance by employing technologies such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and alternative fuels.
Chassis and Suspension: The chassis forms the backbone of a vehicle, providing structural support and ensuring stability. Suspension systems enhance ride comfort and handling characteristics. Engineers work on optimizing chassis design, suspension geometry, and materials to achieve an ideal balance between ride quality and vehicle dynamics.
Safety and Crashworthiness: Safety is a paramount concern in automobile engineering. Engineers integrate advanced safety features like airbags, anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and collision avoidance systems to mitigate the risks associated with accidents.
Vehicle Electronics and Control Systems: Modern vehicles heavily rely on electronics and control systems to manage engine performance, emissions, comfort features, and driver-assistance systems. Automobile engineers work on developing sophisticated electronic control units (ECUs) and software algorithms to improve vehicle efficiency and enhance the driving experience.
III. Technological Advancements:
Electric and Autonomous Vehicles: The emergence of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technologies has brought about a paradigm shift in the automobile industry. Engineers are at the forefront of developing EV technologies, including battery systems, charging infrastructure, and range optimization. Additionally, they are working on advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to enable autonomous driving.
Lightweight Materials: To enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, engineers are exploring lightweight materials like aluminum, carbon fiber composites, and high-strength steel. These materials offer improved structural integrity while reducing the overall weight of the vehicle.
Connectivity and Infotainment: With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), automobiles are becoming increasingly connected. Engineers are integrating advanced infotainment systems, telematics, and wireless communication technologies to provide seamless connectivity and enhance the driving experience.
IV. Future Prospects:
The future of automobile engineering is filled with exciting possibilities. Here are some key areas that hold tremendous potential:
Sustainable Mobility: As the world grapples with climate change, engineers are striving to develop sustainable mobility solutions. This includes further advancements in electric vehicles, hydrogen fuel cells, renewable energy integration, and intelligent transportation systems.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: Engineers are exploring additive manufacturing (3D printing), robotics, and automation to revolutionize the manufacturing process, making it more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly.
Intelligent Transportation Systems: The integration of smart infrastructure, real-time traffic management, and vehicle-to-vehicle/vehicle-to-infrastructure communication systems will enhance safety, reduce congestion, and optimize traffic flow.
Shared and Autonomous Mobility: The sharing economy and autonomous driving technologies are set to reshape the future of transportation. Automobile engineers are at the forefront of developing shared mobility platforms, autonomous fleets, and mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) concepts.
Conclusion:
Automobile engineering has come a long way since its inception, playing a vital role in transforming the way we travel and shaping the future of mobility. From the design of vehicles to the development of advanced technologies, automobile engineers continue to push the boundaries of innovation. With a focus on sustainability, safety, and connectivity, the field is poised to redefine the way we interact with automobiles and revolutionize the transportation industry as a whole.